2023 Issue 7
Mechanism and effects of extramedullary hematopoiesis on anti-tumor immunity
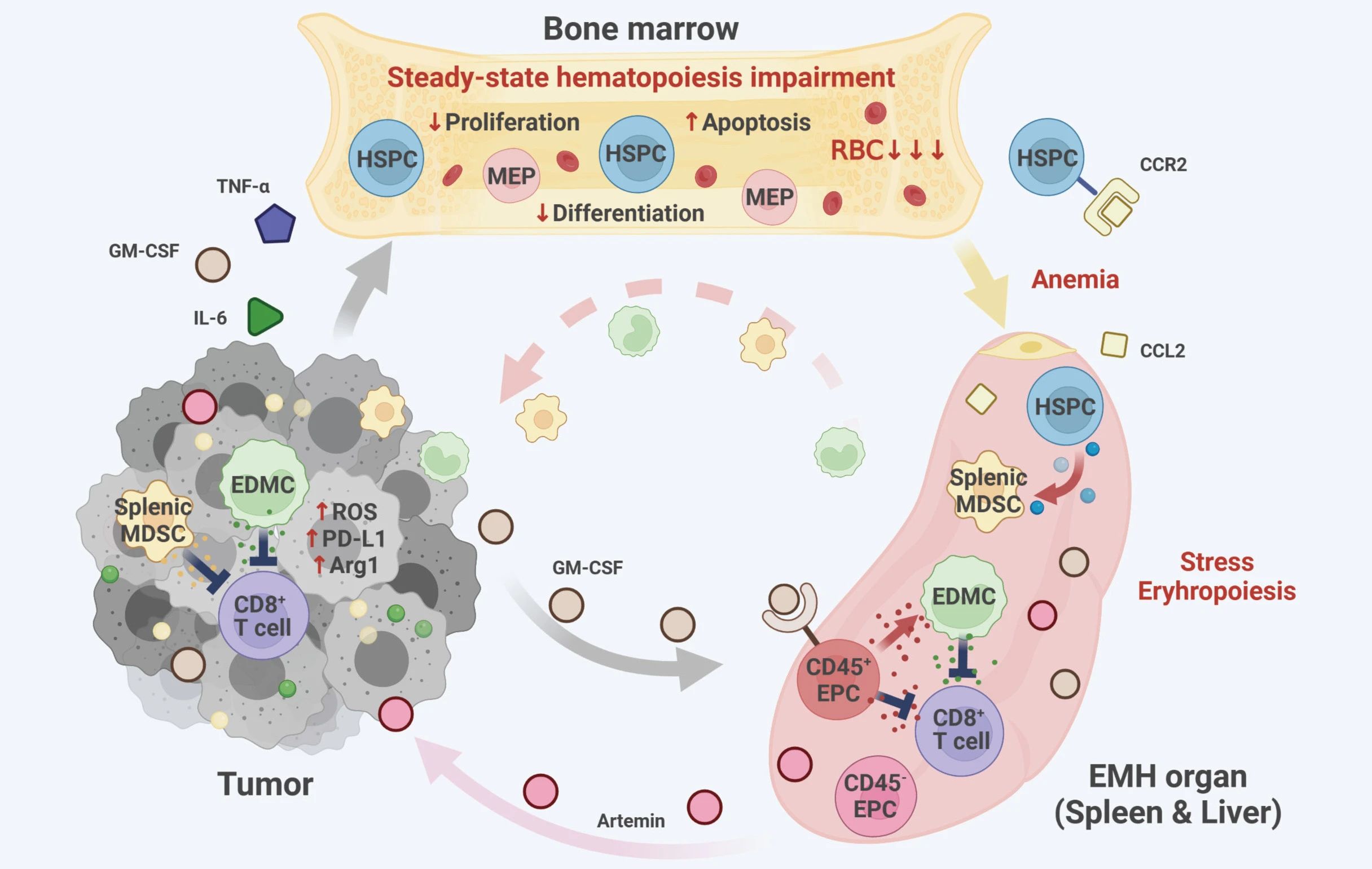
Cancer ’s pervasive presence triggers an inflammatory response that detrimentally impacts bone marrow erythropoiesis, leading to anemia and the emergence of extramedullary hematopoiesis (EMH). In this distinct hematopoietic state, hematopoietic progenitor cells (HSPCs) are recruited to the spleen, where they undergo differentiation into myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Consequently, this process fosters tumor-promoting myelopoiesis and disrupts the immune system’s anti-tumor defenses. Simultaneously, tumor-induced EMH generates a surplus of erythroid progenitor cells (EPCs). Unfortunately, the majority of these EPCs not only fail to support normal hematopoiesis but also acquire pro-tumorigenic properties. Specifically, CD45-EPCs contribute to tumor progression through the secretion of artemin. Furthermore, CD45+EPCs and their derivative cells, known as erythroid-derived suppressor cells (EDMCs), significantly hinder the proliferation and immune function of CD8+ T cells. Consequently, tumor-trained EMH acts as a compensatory mechanism that undermines anti-tumor immunity.
2023 Issue 6
Neutrophils as key regulators of tumor immunity that restrict immune checkpoint blockade in liver cancer
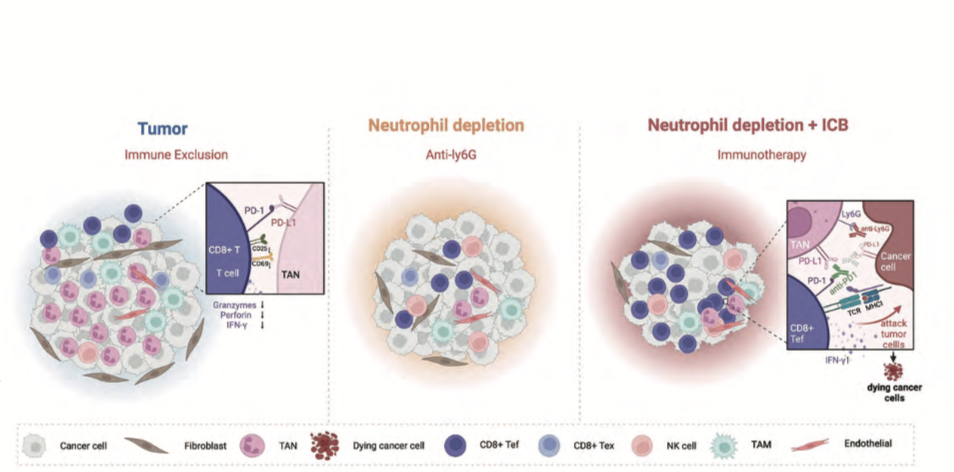
Liver tumors characterized by intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) demonstrated moderate responses to anti-Ly6G treatment, while showing resistance to PD-1 blockade. It is worth noting that depleting neutrophils led to a substantial increase in the infiltration of CD8+ T cells in the tumor microenvironment, accompanied by a significant decrease in exhausted T cells. Moreover, a synergistic therapeutic approach combining anti-Ly6G and anti-PD-L1 agents markedly enhanced the infiltration of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, resulting in a remarkable reduction in tumor burden.
2023 Issue 5
Nanomedicine-based combination therapies for overcoming temozolomide resistance in glioblastomas
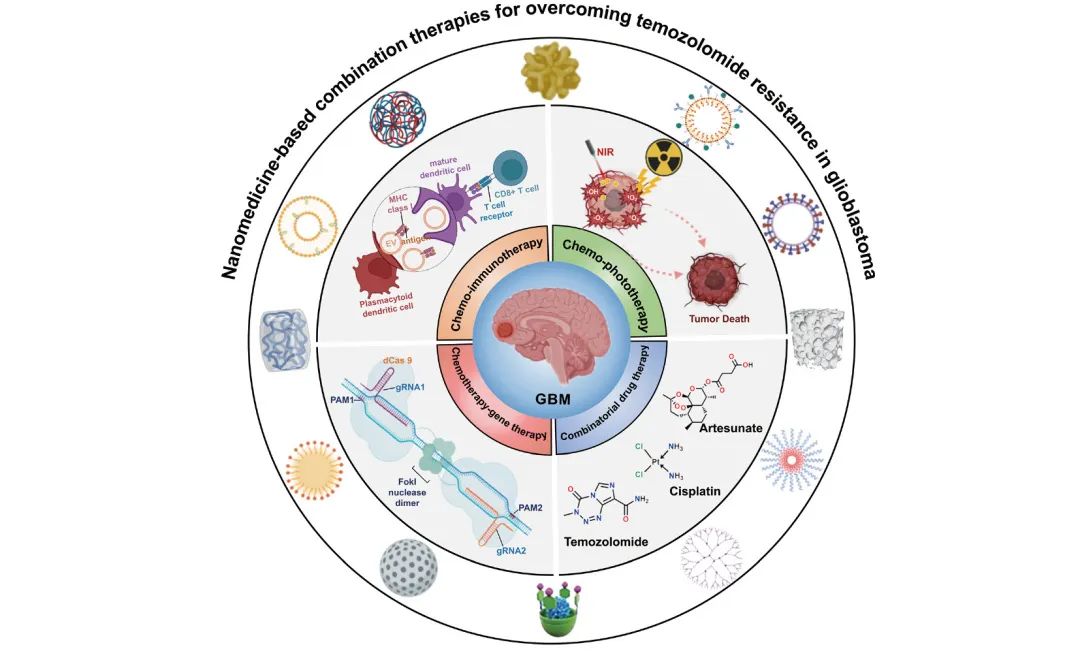
Temozolomide (TMZ) is the first-line chemotherapeutic drug for glioblastoma (GBM) treatment which is troubled by its severe resistance developed by multiple mechanisms including reduced drug uptake, increased drug efflux, DNA damage repair, and heterogeneous tumor microenvironment. As these drug resistances involve in complicated signal networks and various compensatory mechanisms, combination therapy that targets multiple pathogenic pathways is an attractive strategy to address drug resistance and improve chemosensitivity of GBM. Currently, nanotechnology has provided new opportunities for GBM treatment through improving blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability and GBM accumulation. Moreover, drug delivery system could be elaborately designed to load multiple therapeutics and further optimized to maximize the therapeutic efficiency of combination therapies, including combination chemotherapy, chemotherapy-gene therapy, chemo-phototherapy, and chemoimmunotherapy.
2023 Issue 4
Facing challenges with hope: universal immune cells for hematologic malignancies
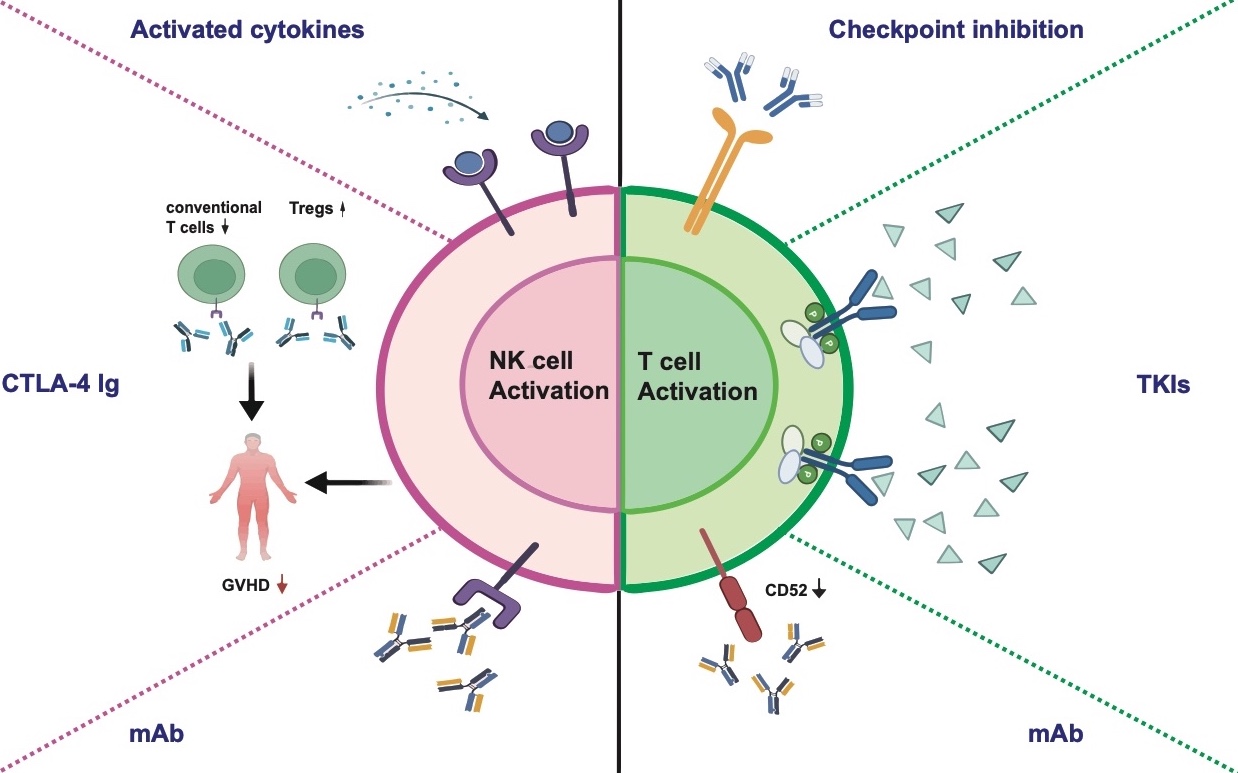
As allogenic cells, universal immune cells are rarely rejected by the host immune system and always lead to transplantation tolerance. Thanks to their special immune tolerance characteristics and anti-tumor ability, universal immune cells are possible candidates for allogenic transplantation. However, the proliferation and persistence efficacy of universal immune cells warrant improvement. The combination of activated cytokines, checkpoint inhibition, CTLA-4 Ig, anti-CD52 antibodies, and TKIs may improve the clinical efficacy of universal immune cells.
2023 Issue 3
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a complex assembly of genetically heterogeneous cancer cells and different cell types that constitute the local environment; however, the interactions among these factors in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remain unclear. Investigations on tumor immunity and host defense in patients with PDAC demonstrate promising results for immunotherapy. Therefore, an ‘anti-/pro-tumor model’ defined by an established host-related ‘anti-tumor’ factor (CD8+ T lymphocytes) and ‘pro- tumor’ factors (cancer stem cells and tumor buddings) was established based on the artificial intelligence-based comprehensive analysis, and then its prognostic significance in PDAC was clarified. In addition, the spatial distribution among these factors in the TME of PDAC was also illustrated. As a visual representation of the hazard ratios of multiple prognostic factors, a nomogram model based on the ‘anti-/pro-tumor model’ was constructed.
2023 Issue 2
Intercellular transmission of cGAS-STING signaling in cancer
The beneficial roles of cGAS-STING signaling in tumorigenesis and progression have recently gained considerable attention. Immune and tumor cells use the cGAS-STING mechanism to sense and respond to genomic instability, DNA damage, and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by extra- and intracellular stresses. The effective intercellular transmission of cGAS-STING signaling through various modes including internalization, extracellular vesicle, gap junction, membrane fusion, non-canonical autophagy and ligand-receptor system enables the sharing of critical information arising from infected, injured, or cancerous cells and the activation of multiple bystander cells in innate immune responses. In cancers, intercellular transfer of cGAS-STING signaling elements like dsDNA, cGAMP, activated STING connects the tumor microenvironment with pathogenic, immune, and stromal cells, thus promoting or compromising various immune responses and substantially altering disease progression. Consequently, leveraging the intercellular transmission of cGAS-STING signaling might serve as a promising target for developing therapeutics against malignancy.
2023 Issue 1
Major roles of the circadian clock in cancer
Circadian is a natural rhythm that widely exists in all creatures and regulates the process and physiological functions of various biochemical reactions. The circadian clock is critical for cancer occurrence and progression. Its function is regulated by metabolic activities, expression, and transcription of various genes. The CLOCK-BMAL1 complex is an integral part of this rhythm, like a hard-working farmer, working on a specific schedule. At the initial stage of circadian clock, the E-box cannot be activated due to the inhibition of negative regulators such as CRY, but after a period of light, CRY is separated from it, and the CLOCK-BMAL1 complex begins its biological function.