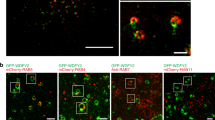
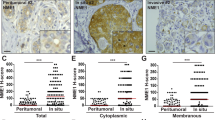
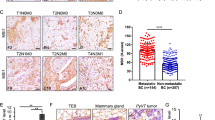
Abstract
NEDD9 is an established marker of invasive and metastatic cancers. NEDD9 downregulation has been shown to dramatically reduce cell invasion and metastasis in multiple tumors. The mechanisms by which NEDD9 regulates invasion are largely unknown. In the current study, we have found that NEDD9 is required for matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14) enzymatic recovery/recycling through the late endosomes to enable disengagement of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP2) and tumor invasion. Depletion of NEDD9 decreases targeting of the MMP14/TIMP2 complex to late endosomes and increases trafficking of MMP14 from early/sorting endosomes back to the surface in a small GTPase ADP ribosylation factor-6 (Arf6)-dependent manner. NEDD9 directly binds to Arf6-GTPase-activating protein, ARAP3 and Arf6-effector GGA3, thereby facilitating the Arf6 inactivation required for MMP14/TIMP2 targeting to late endosomes. Re-expression of NEDD9 or a decrease in Arf6 activity is sufficient to restore MMP14 activity and the invasive properties of tumor cells. Importantly, NEDD9 inhibition by Vivo-Morpholinos, an antisense therapy, decreases primary tumor growth and metastasis in xenograft models of breast cancer. Collectively, our findings uncover a novel mechanism to control tumor-cell dissemination through NEDD9/Arf6-dependent regulation of MMP14/TIMP2 trafficking, and validate NEDD9 as a clinically relevant therapeutic target to treat metastatic cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim M, Gans JD, Nogueira C, Wang A, Paik JH, Feng B et al. Comparative oncogenomics identifies NEDD9 as a melanoma metastasis gene. Cell 2006; 125: 1269–1281.
Kondo S, Iwata S, Yamada T, Inoue Y, Ichihara H, Kichikawa Y et al. Impact of the integrin signaling adaptor protein NEDD9 on prognosis and metastatic behavior of human lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2012; 18: 6326–6338.
Speranza MC, Frattini V, Pisati F, Kapetis D, Porrati P, Eoli M et al. NEDD9, a novel target of miR-145, increases the invasiveness of glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2012; 3: 723–734.
Ahn J, Sanz-Moreno V, Marshall CJ . The metastasis gene NEDD9 product acts through integrin beta3 and Src to promote mesenchymal motility and inhibit amoeboid motility. J Cell Sci 2012; 125: 1814–1826.
O'Neill GM, Seo S, Serebriiskii IG, Lessin SR, Golemis EA . A new central scaffold for metastasis: parsing HEF1/Cas-L/NEDD9. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 8975–8979.
Little JL, Serzhanova V, Izumchenko E, Egleston BL, Parise E, Klein-Szanto AJ et al. A requirement for Nedd9 in luminal progenitor cells prior to mammary tumorigenesis in MMTV-HER2/ErbB2 mice. Oncogene 2013; 33: 411–420.
Ice RJ, McLaughlin SL, Livengood RH, Culp MV, Eddy ER, Ivanov AV et al. NEDD9 depletion destabilizes Aurora A kinase and heightens the efficacy of Aurora A inhibitors: implications for treatment of metastatic solid tumors. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3168–3180.
Lucas JT Jr, Salimath BP, Slomiany MG, Rosenzweig SA . Regulation of invasive behavior by vascular endothelial growth factor is HEF1-dependent. Oncogene 2010; 29: 4449–4459.
Jin Y, Li F, Zheng C, Wang Y, Fang Z, Guo C et al. NEDD9 promotes lung cancer metastasis through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Cancer 2013; 134: 2294–2304.
McLaughlin SL, Ice RJ, Rajulapati A, Kozyulina PY, Livengood RH, Kozyreva VK et al. NEDD9 Depletion leads to MMP14 inactivation by TIMP2 and prevents invasion and metastasis. Mol Cancer Res 2013; 12: 69–81.
Maquoi E, Frankenne F, Baramova E, Munaut C, Sounni NE, Remacle A et al. Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-associated degradation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 in human tumor cell lines. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 11368–11378.
Remacle A, Murphy G, Roghi C . Membrane type I-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) is internalised by two different pathways and is recycled to the cell surface. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 3905–3916.
Zucker S, Hymowitz M, Conner C, DeClerck Y, Cao J . TIMP-2 is released as an intact molecule following binding to MT1-MMP on the cell surface. Exp Cell Res 2004; 293: 164–174.
Wang X, Ma D, Keski-Oja J, Pei D . Co-recycling of MT1-MMP and MT3-MMP through the trans-Golgi network. Identification of DKV582 as a recycling signal. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 9331–9336.
Hakulinen J, Sankkila L, Sugiyama N, Lehti K, Keski-Oja J . Secretion of active membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-14) into extracellular space in microvesicular exosomes. J Cell Biochem 2008; 105: 1211–1218.
Williams KC, Coppolino MG . Phosphorylation of membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) and its vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 (VAMP7)-dependent trafficking facilitate cell invasion and migration. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 43405–43416.
D'Souza-Schorey C, Chavrier P . ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 347–358.
Anders N, Jurgens G . Large ARF guanine nucleotide exchange factors in membrane trafficking. Cell Mol Life Sci 2008; 65: 3433–3445.
Sakagami H . The EFA6 family: guanine nucleotide exchange factors for ADP ribosylation factor 6 at neuronal synapses. Tohoku J Exp Med 2008; 214: 191–198.
Spang A, Shiba Y, Randazzo PA . Arf GAPs: gatekeepers of vesicle generation. FEBS Lett 2010; 584: 2646–2651.
Netzel-Arnett S, Mallya SK, Nagase H, Birkedal-Hansen H, Van Wart HE . Continuously recording fluorescent assays optimized for five human matrix metalloproteinases. Anal Biochem 1991; 195: 86–92.
Uekita T, Itoh Y, Yana I, Ohno H, Seiki M . Cytoplasmic tail-dependent internalization of membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is important for its invasion-promoting activity. J Cell Biol 2001; 155: 1345–1356.
Anilkumar N, Uekita T, Couchman JR, Nagase H, Seiki M, Itoh Y . Palmitoylation at Cys574 is essential for MT1-MMP to promote cell migration. FASEB J 2005; 19: 1326–1328.
Yu X, Zech T, McDonald L, Gonzalez EG, Li A, Macpherson I et al. N-WASP coordinates the delivery and F-actin-mediated capture of MT1-MMP at invasive pseudopods. J Cell Biol 2012; 199: 527–544.
Worthylake R, Opresko LK, Wiley HS . ErbB-2 amplification inhibits downregulation and induces constitutive activation of both ErbB-2 and epidermal growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 8865–8874.
Brown FD, Rozelle AL, Yin HL, Balla T, Donaldson JG . Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate and Arf6-regulated membrane traffic. J Cell Biol 2001; 154: 1007–1017.
Radhakrishna H, Klausner RD, Donaldson JG . Aluminum fluoride stimulates surface protrusions in cells overexpressing the ARF6 GTPase. J Cell Biol 1996; 134: 935–947.
Parachoniak CA, Luo Y, Abella JV, Keen JH, Park M . GGA3 functions as a switch to promote Met receptor recycling, essential for sustained ERK and cell migration. Dev Cell 2011; 20: 751–763.
Gu JJ, Lavau CP, Pugacheva E, Soderblom EJ, Moseley MA, Pendergast AM . Abl family kinases modulate T cell-mediated inflammation and chemokine-induced migration through the adaptor HEF1 and the GTPase Rap1. Sci Signal 2012; 5: ra51.
Sanz-Moreno V, Gadea G, Ahn J, Paterson H, Marra P, Pinner S et al. Rac activation and inactivation control plasticity of tumor cell movement. Cell 2008; 135: 510–523.
Peters PJ, Hsu VW, Ooi CE, Finazzi D, Teal SB, Oorschot V et al. Overexpression of wild-type and mutant ARF1 and ARF6: distinct perturbations of nonoverlapping membrane compartments. J Cell Biol 1995; 128: 1003–1017.
Hafner M, Schmitz A, Grune I, Srivatsan SG, Paul B, Kolanus W et al. Inhibition of cytohesins by SecinH3 leads to hepatic insulin resistance. Nature 2006; 444: 941–944.
Radisky ES, Radisky DC . Matrix metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 2010; 15: 201–212.
Schmid S, Fuchs R, Kielian M, Helenius A, Mellman I . Acidification of endosome subpopulations in wild-type Chinese hamster ovary cells and temperature-sensitive acidification-defective mutants. J Cell Biol 1989; 108: 1291–1300.
Blick T, Widodo E, Hugo H, Waltham M, Lenburg ME, Neve RM et al. Epithelial mesenchymal transition traits in human breast cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis 2008; 25: 629–642.
Friedl P, Locker J, Sahai E, Segall JE . Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol 2012; 14: 777–783.
Giampieri S, Pinner S, Sahai E . Intravital imaging illuminates transforming growth factor beta signaling switches during metastasis. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 3435–3439.
Zhong J, Baquiran JB, Bonakdar N, Lees J, Ching YW, Pugacheva E et al. NEDD9 stabilizes focal adhesions, increases binding to the extra-cellular matrix and differentially effects 2D versus 3D cell migration. PloS One 2012; 7: e35058.
Cabodi S, del Pilar Camacho-Leal M, Di Stefano P, Defilippi P . Integrin signalling adaptors: not only figurants in the cancer story. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 858–870.
Hemmann S, Graf J, Roderfeld M, Roeb E . Expression of MMPs and TIMPs in liver fibrosis - a systematic review with special emphasis on anti-fibrotic strategies. J Hepatol 2007; 46: 955–975.
Oblander SA, Zhou Z, Galvez BG, Starcher B, Shannon JM, Durbeej M et al. Distinctive functions of membrane type 1 matrix-metalloprotease (MT1-MMP or MMP-14) in lung and submandibular gland development are independent of its role in pro-MMP-2 activation. Dev Biol 2005; 277: 255–269.
Polette M, Nawrocki-Raby B, Gilles C, Clavel C, Birembaut P . Tumour invasion and matrix metalloproteinases. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2004; 49: 179–186.
McLaughlin SL, Ice RJ, Rajulapati A, Kozyulina PY, Livengood RH, Kozyreva VK et al. NEDD9 depletion leads to MMP14 inactivation by TIMP2 and prevents invasion and metastasis. Mol Cancer Res 2014; 12: 69–81.
Remacle AG, Rozanov DV, Fugere M, Day R, Strongin AY . Furin regulates the intracellular activation and the uptake rate of cell surface-associated MT1-MMP. Oncogene 2006; 25: 5648–5655.
Cai D, Felekkis KN, Near RI, O'Neill GM, van Seventer JM, Golemis EA et al. The GDP exchange factor AND-34 is expressed in B cells, associates with HEF1, and activates Cdc42. J Immunol 2003; 170: 969–978.
Schweitzer JK, Sedgwick AE, D'Souza-Schorey C . ARF6-mediated endocytic recycling impacts cell movement, cell division and lipid homeostasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2011; 22: 39–47.
Paleotti O, Macia E, Luton F, Klein S, Partisani M, Chardin P et al. The small G-protein Arf6GTP recruits the AP-2 adaptor complex to membranes. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 21661–21666.
Sabe H, Hashimoto S, Morishige M, Ogawa E, Hashimoto A, Nam JM et al. The EGFR-GEP100-Arf6-AMAP1 signaling pathway specific to breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Traffic 2009; 10: 982–993.
Santy LC, Ravichandran KS, Casanova JE . The DOCK180/Elmo complex couples ARNO-mediated Arf6 activation to the downstream activation of Rac1. Curr Biol 2005; 15: 1749–1754.
Fang Z, Miao Y, Ding X, Deng H, Liu S, Wang F et al. Proteomic identification and functional characterization of a novel ARF6 GTPase-activating protein, ACAP4. Mol Cell Proteomics 2006; 5: 1437–1449.
Aikawa Y, Martin TF . ARF6 regulates a plasma membrane pool of phosphatidylinositol(4,5)bisphosphate required for regulated exocytosis. J Cell Biol 2003; 162: 647–659.
Shteyn E, Pigati L, Folsch H . Arf6 regulates AP-1B-dependent sorting in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 2011; 194: 873–887.
Radhakrishna H, Donaldson JG . ADP-ribosylation factor 6 regulates a novel plasma membrane recycling pathway. J Cell Biol 1997; 139: 49–61.
Radhakrishna H, Al-Awar O, Khachikian Z, Donaldson JG . ARF6 requirement for Rac ruffling suggests a role for membrane trafficking in cortical actin rearrangements. J Cell Sci 1999; 112: 855–866.
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Marrero-Diaz R, Megias D, Genis L, Garcia-Grande A, Garcia MA et al. MT1-MMP proinvasive activity is regulated by a novel Rab8-dependent exocytic pathway. EMBO J 2007; 26: 1499–1510.
Hattula K, Furuhjelm J, Tikkanen J, Tanhuanpaa K, Laakkonen P, Peranen J . Characterization of the Rab8-specific membrane traffic route linked to protrusion formation. J Cell Sci 2006; 119: 4866–4877.
Holmbeck K, Bianco P, Caterina J, Yamada S, Kromer M, Kuznetsov SA et al. MT1-MMP-deficient mice develop dwarfism, osteopenia, arthritis, and connective tissue disease due to inadequate collagen turnover. Cell 1999; 99: 81–92.
Pahwa S, Stawikowski MJ, Fields GB . Monitoring and inhibiting MT1-MMP during cancer initiation and progression. Cancers (Basel) 2014; 6: 416–435.
Strongin AY . Proteolytic and non-proteolytic roles of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase in malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010; 1803: 133–141.
Vonderheit A, Helenius A . Rab7 associates with early endosomes to mediate sorting and transport of Semliki forest virus to late endosomes. PLoS Biol 2005; 3: e233.
Clark ES, Whigham AS, Yarbrough WG, Weaver AM . Cortactin is an essential regulator of matrix metalloproteinase secretion and extracellular matrix degradation in invadopodia. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 4227–4235.
Pugacheva EN, Golemis EA . The focal adhesio n scaffolding protein HEF1 regulates activation of the Aurora-A and Nek2 kinases at the centrosome. Nat Cell Biol 2005; 7: 937–946.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mrs Yoho and Drs Schaller and Weed for critically reading the manuscript and providing administrative support during manuscript preparation. We also thank the West Virginia University Microscope Imaging Facility, supported by the Mary Babb Randolph Cancer Center and NIH grants P20 RR016440, P30 RR032138/GM103488 and P20 RR016477. The WVU Flow Cytometry Core Facility was supported by NIH grants P30 GM103488, P30 RR032138 and RCP1101809. We also thank Mr Farrugia for his assistance in the analysis of the microarray data. This work was supported by grants from the NIH-NCI (CA148671 to ENP), the Susan G Komen For the Cure Foundation (KG100539 to ENP) and in part by NIH/NCRR (5 P20 RR016440-09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loskutov, Y., Kozyulina, P., Kozyreva, V. et al. NEDD9/Arf6-dependent endocytic trafficking of matrix metalloproteinase 14: a novel mechanism for blocking mesenchymal cell invasion and metastasis of breast cancer. Oncogene 34, 3662–3675 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.297
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.297
This article is cited by
-
Vesicular trafficking–related proteins as the potential therapeutic target for breast cancer
Protoplasma (2020)
-
ZMYND10, an epigenetically regulated tumor suppressor, exerts tumor-suppressive functions via miR145-5p/NEDD9 axis in breast cancer
Clinical Epigenetics (2019)
-
CLIC4 regulates late endosomal trafficking and matrix degradation activity of MMP14 at focal adhesions in RPE cells
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
LPA signaling is regulated through the primary cilium: a novel target in glioblastoma
Oncogene (2018)