Abstract
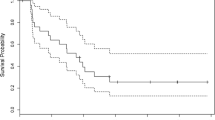
Approximately 40–50% of glioblastomas (GBM) overexpress epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Erlotinib is a specific and potent EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor active against refractory GBM. Patients with non-small cell lung cancer and ≥grade 2 erlotinib-induced rash have improved survival. This phase 2 study assessed the efficacy and safety of concurrent radiation therapy (RT) and temozolomide with pharmacodynamic dose escalation of erlotinib in patients with newly diagnosed GBM. Patients received RT 60 Gy in 30 fractions with concurrent temozolomide 75 mg/m2/day × 42 days, followed in four weeks by temozolomide 150–200 mg/m2/day × 5, every 28 days for 12 cycles. Patients received erlotinib, 50 mg/day and increased by 50 mg/day every 2 weeks until the occurrence of grade 2 rash or to a maximum dose of 150 mg/day, from day 1 until disease progression. Twenty-seven patients were treated in this study. Twenty-two (81%) patients came off study for progressive disease (18 [67%]) or adverse events (4 [15%]). Eighteen patients (67%) have died. Median progression-free survival was 2.8 months, and the median overall survival was 8.6 months. Five patients remain on study with a median follow-up of 16 months. Grade 3/4 toxicities included thrombocytopenia, anemia, lymphopenia, fatigue, and febrile neutropenia. There were four deaths on study, three definitely treatment-related; therefore, the trial was terminated after accrual of 27 of 30 planned patients. Erlotinib co administered with RT and temozolomide was not efficacious and had an unacceptable toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Henson JW (2006) Treatment of glioblastoma multiforme: a new standard. Arch Neurol 63:337–341
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Stewart LA (2002) Chemotherapy in adult high-grade glioma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data from 12 randomised trials. Lancet 359:1011–1018
Libermann TA, Nusbaum HR, Razon N et al (1985) Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours of glial origin. Nature 313:144–147
Schlegel J, Merdes A, Stumm G et al (1994) Amplification of the epidermal-growth-factor-receptor gene correlates with different growth behaviour in human glioblastoma. Int J Cancer 56:72–77
Tang P, Steck PA, Yung WK (1997) The autocrine loop of TGF-alpha/EGFR and brain tumors. J Neurooncol 35:303–314
Halatsch ME, Gehrke E, Borhani FA et al (2003) EGFR but not PDGFR-beta expression correlates to the antiproliferative effect of growth factor withdrawal in glioblastoma multiforme cell lines. Anticancer Res 23:2315–2320
Lund-Johansen M, Bjerkvig R, Humphrey PA, Bigner SH, Bigner DD, Laerum OD (1990) Effect of epidermal growth factor on glioma cell growth, migration, and invasion in vitro. Cancer Res 50:6039–6044
Shinojima N, Tada K, Shiraishi S et al (2003) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 63:6962–6970
Barker FG II, Simmons ML, Chang SM et al (2001) EGFR overexpression and radiation response in glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:410–418
Chakravarti A, Chakladar A, Delaney MA, Latham DE, Loeffler JS (2002) The epidermal growth factor receptor pathway mediates resistance to sequential administration of radiation and chemotherapy in primary human glioblastoma cells in a RAS-dependent manner. Cancer Res 62:4307–4315
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J et al. (2005) Erlotinib improves survival when added to gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. A phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (NCIC-CTG). 2005 Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2005:121. Abstract 77. Available at http://www.asco.org
Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T et al (2005) Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353:123–132
Halatsch ME, Gehrke EE, Vougioukas VI et al (2004) Inverse correlation of epidermal growth factor receptor messenger RNA induction and suppression of anchorage-independent growth by OSI-774, an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in glioblastoma multiforme cell lines. J Neurosurg 100:523–533
Iwata KK, Provoncha K, Gibson N (2002) Inhibition of mutant EGFRvIII transformed cells by tyrosine kinase inhibitor OSI-774 (Tarceva). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 21:Abstract 79
Prados MD, Lamborn KR, Chang S et al (2006) Phase 1 study of erlotinib HCl alone and combined with temozolomide in patients with stable or recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol 8:67–78
Vogelbaum MA, Peereboom D, Stevens G, Barnett GH, Brewer C (2004) Response rate to single agent therapy with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: results of a phase II study. In: Proceedings of the ninth meeting of the society for neuro-oncology 384. Abstract TA-59
Krishnan S, Brown PD, Ballman KV et al (2006) Phase I trial of erlotinib with radiation therapy in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: results of North Central Cancer Treatment Group protocol N0177. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 65:1192–1199 Epub 2006 Apr 19
Perez-Soler R, Chachoua A, Hammond LA et al (2004) Determinants of tumor response and survival with erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:3238–3247
Grossman SA, O’Neill A, Grunnet M, Mehta M, Pearlman JL, Wagner H et al (2003) Phase III study comparing three cycles of infusional carmustine, cisplatin followed by radiation therapy with radiation therapy, concurrent carmustine in patients with newly diagnosed supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial 2394. J Clin Oncol 21(8):1485–1491
Barrie M, Couprie C, Dufour H, Figarella-Branger D, Muracciole X, Hoang-Xuan K et al (2005) Temozolomide in combination with BCNU before and after radiotherapy in patients with inoperable newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. Ann Oncol 16(7):1177–1184
Levin VA, Phuphanich S, Yung WK, Forsyth PA, Maestro RD, Perry JR et al (2006) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of marimastat in glioblastoma multiforme patients following surgery and irradiation. J Neurooncol 78(3):295–302
Parkinson JF, Wheeler HR, Clarkson A et al (2008) Variation of O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation in serial samples in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 87:71–78
Curran WJ Jr, Scott CB, Horton J, Nelson JS, Weinstein AS, Fischbach AJ et al (1993) Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group malignant glioma trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(9):704–710
Chamberlain MC, Glantz MJ, Chalmers L, Van Horn A, Sloan AE (2007) Early necrosis following concurrent Temodar and radiotherapy in patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 82:81–83
Franceschi E, Cavallo G, Lonardi S et al (2007) Gefitinib in patients with progressive high-grade gliomas: a multicentre phase II study by Gruppo Italiano Cooperativo di Neuro-Oncologia (GICNO). Br J Cancer 96:1047–1051
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I et al (2005) Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med 353:2012–2024
Rich JN, Reardon DA, Peery T et al (2004) Phase II trial of gefitinib in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 22:133–142 Epub 2003 Nov 24
Stea B, Falsey R, Kislin K et al (2003) Time and dose-dependent radiosensitization of the glioblastoma multiforme U251 cells by the EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (‘Iressa’). Cancer Lett 202:43–51
Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C et al (2004) Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol 22:777–784
Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH et al (2004) Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol 22:785–794
Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R et al (2005) TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:5892–5899 Epub 2005 Jul 25
Stommel JM, Kimmelman AC, Ying H et al (2007) Coactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases affects the response of tumor cells to targeted therapies. Science 318:287–290
Solit DB, She Y, Lobo J et al (2005) Pulsatile administration of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib is significantly more effective than continuous dosing for sensitizing tumors to paclitaxel. Clin Cancer Res 11:1983–1989
Li T, Ling YH, Goldman ID, Perez-Soler R (2007) Schedule-dependent cytotoxic synergism of pemetrexed and erlotinib in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 13:3413–3422
Piperdi B, Ling YH, Perez-Soler R (2007) Schedule-dependent interaction between the proteosome inhibitor bortezomib and the EGFR-TK inhibitor erlotinib in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. J Thorac Oncol 2:715–721
Hirose Y, Berger MS, Pieper RO (2001) p53 effects both the duration of G2/M arrest and the fate of temozolomide-treated human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 61:1957–1963
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Godard S et al (2004) Clinical trial substantiates the predictive value of O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation in glioblastoma patients treated with temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res 10:1871–1874
Learn CA, Hartzell TL, Wikstrand CJ et al (2004) Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition by mutant epidermal growth factor receptor variant III contributes to the neoplastic phenotype of glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res 10:3216–3224
Bach JP, Kiessling AM, Kleinhans A et al (2006) Pulmonary fibrosis in a patient treated with erlotinib. Onkologie 29:342–343 Epub 2006 Jul 3
Prados MD, Chang SM, Butowski N et al (2009) Phase II study of erlotinib plus temozolomide during and after radiation therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme or gliosarcoma. J Clin Oncol 27:579–584
Brown PD, Krishnan S, Sarkaria JN et al (2008) Phase I/II trial of erlotinib and temozolomide with radiation therapy in the treatment of newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: North Central Cancer Treatment Group Study N0177. J Clin Oncol 26:5603–5609
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peereboom, D.M., Shepard, D.R., Ahluwalia, M.S. et al. Phase II trial of erlotinib with temozolomide and radiation in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 98, 93–99 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0067-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-009-0067-2