Abstract
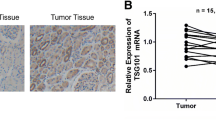
Survivin, an important inhibitor of apoptosis, has been found to play an important role in the initiation, progression, and chemoradioresistance of human malignancies. Previously, we have reported that upregulation of survivin in oral squamous cell carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis and chemoresistance. The aim of this study was to assess prognostic significance of survivin protein expression in RCC and analyze its correlation with radiosensitivity of RCC cells. RT-PCR and Western blot assays were performed to detect survivin mRNA and protein expression in normal human kidney epithelial cell line (HKEC) or RCC cell lines. The expression of survivin mRNA in RCC and corresponding nontumor kidney tissues was also detected by RT-PCR. Immunohistochemistry was performed to determine survivin protein expression in 75 cases of RCC tissue samples. Moreover, the association of survivin protein expression with clinicopathogical factors and prognosis of RCC patients was statistically analyzed. Small interfering RNA was used to knockdown the endogenous survivin expression in RCC cell line (ACHN) and evaluate the effects of survivin knockdown on proliferation, apoptosis, and radiosensitivity of RCC cell line. RCC cells showed sufficient expression of survivin mRNA and protein, but the expression of survivin gene was not detected in normal HKEC. Moreover, the expression level of survivin mRNA in RCC tissues was significantly higher than that in corresponding nontumor kidney tissues. The immunostaining of survivin protein was mainly located in cytoplasm of RCC tumor cells. Tumor pathological stage (P = 0.028), grade (P = 0.004), and lymph node metastasis (P = 0.017) of RCC patients were significantly correlated with survivin protein expression. In addition, patients with high survivin levels had a significantly shorter overall survival than those with low levels (P < 0.001), and the expression of survivin protein was an independent prognostic factor for RCC patients (P = 0.008). The expression of survivin gene could be reduced in RCC cell line and survivin knockdown could inhibit growth and enhance in vivo radiosensitivity of RCC cell line by inducing apoptosis enhancement. Taken together, the status of survivin protein expression may be an independent factor for predicting the prognosis of RCC patients and tumor-specific survivin knockdown combined with radiotherapy will be a potential strategy for RCC therapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55:74–108
Buzaid AC, Todd MB (1989) Therapeutic options in renal cell carcinoma. Semin Oncol 16(Suppl 6):12–16
Altieri DC (2003) Survivin, versatilemodulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene 22:8581–8589
Chau GY, Lee AF, Tsay SH et al (2007) Clinicopathological significance of survivin expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Histopathology 51:204–218
Chen WC, Liu Q, Fu JX et al (2004) Expression of survivin and its significance in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 10:2886–2889
Falleni M, Pellegrini C, Marchetti A et al (2003) Survivin gene expression in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J Pathol 200:620–626
Sarela AI, Verbeke CS, Ramsdale J et al (2002) Expression of survivin, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis and cell cycle regulatory protein, in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer 86:886–892
Osaka E, Suzuki T, Osaka S et al (2006) Survivin as a prognostic factor for osteosarcoma patients. Acta Histochem Cytochem 39:95–100
Asanuma K, Kobayashi D, Furuya D et al (2002) A role for survivin in radioresistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:1057–1062
Rödel F, Hoffmann J, Distel L et al (2005) Survivin as a radioresistance factor, and prognostic and therapeutic target for radiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Res 65:4881–4887
Motzer RJ, Bander NH, Nanus DM (1996) Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 335:865–875
La Casse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG et al (1998) The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene 17:3247–3259
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS et al (1997) X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell death proteases. Nature 388:300–304
Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins: suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:239–252
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC (1997) A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med 3:917–921
Johnson ME, Howerth EW (2004) Survivin: a bifunctional inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Vet Pathol 41:599–607
Nouraee N, Mowla SJ, Ozhand A et al (2009) Expression of survivin and its spliced variants in bladder tumors as a potential prognostic marker. Urol J 6:101–108
Fields AC, Cotsonis G, Sexton D et al (2004) Survivin expression in hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with proliferation, prognostic parameters, and outcome. Mod Pathol 17:1378–1385
Cohen C, Lohmann CM, Cotsonis G et al (2003) Survivin expression in ovarian carcinoma: correlation with apoptotic markers and prognosis. Mod Pathol 16:574–583
Song KY, Jung CK, Park WS et al (2009) Expression of the antiapoptosis gene Survivin predicts poor prognosis of stage III gastric adenocarcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol 39:290–296
Troeger A, Siepermann M, Escherich G et al (2007) Survivin and its prognostic significance in pediatric acute B-cell precursor lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 92:1043–1050
Adida C, Recher C, Raffoux E et al (2000) Expression and prognostic significance of survivin in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 111:196–203
Virrey JJ, Guan S, Li W et al (2008) Increased survivin expression confers chemoresistance to tumor-associated endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 173:575–585
Yuan QZ, Wang CT, Mao YQ et al (2010) Enhanced tumor radiosensitivity by a survivin dominant-negative mutant. Oncol Rep 23:97–103
Zaffaroni N, Daidone MG (2002) Survivin expression and resistance to anticancer treatments: perspectives for new therapeutic interventions. Drug Resist Updat 5:65–72
Ryan BM, O’Donovan N, Duffy MJ (2009) Survivin: a new target for anti-cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev 35:553–562
Kami K, Doi R, Koizumi M et al (2005) Downregulation of survivin by siRNA diminishes radioresistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Surgery 138:299–305
Shen J, Liu J, Long Y et al (2009) Knockdown of survivin expression by siRNAs enhances chemosensitivity of prostate cancer cells and attenuates its tumorigenicity. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 41:223–230
Sato A, Ito K, Asano T et al (2007) Synergistic effect of survivin-specific small interfering RNA and topotecan in renal cancer cells: topotecan enhances liposome-mediated transfection by increasing cellular uptake. Int J Oncol 30:670–695
Song X, Wang JB, Yin DL et al (2009) Down-regulation of lung resistance related protein by RNA interference targeting survivin induces the reversal of chemoresistances in hepatocellular carcinoma. Chin Med J 122:2636–2642
Fulda S, Debatin KM (2004) Sensitization for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis by the chemopreventive agent resveratrol. Cancer Res 64:337–346
Zamparese R, Pannone G, Santoro A et al (2008) Survivin expression in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Invest 26:929–935
Byun SS, Yeo WG, Lee SE et al (2007) Expression of survivin in renal cell carcinomas: association with pathologic features and clinical outcome. Urology 69(1):34–37
Acknowledgment
The authors thank the Members of Department of Pathology in Xijing Hospital for their sincere help and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yu Lei and Zhang Geng are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, Y., Geng, Z., Guo-Jun, W. et al. Prognostic significance of survivin expression in renal cell cancer and its correlation with radioresistance. Mol Cell Biochem 344, 23–31 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0525-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-010-0525-3