Abstract
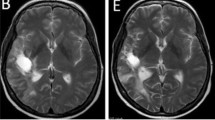
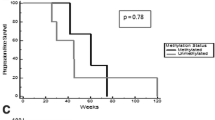
We determined the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) and dose-limiting toxicities (DLT) of the oral vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) inhibitor, sunitinib, when administered with irinotecan among recurrent malignant glioma (MG) patients. For each 42-day cycle, sunitinib was administered once a day for four consecutive weeks followed by a 2 week rest. Irinotecan was administered intravenously every other week. Each agent was alternatively escalated among cohorts of 3–6 patients enrolled at each dose level. Patients on CYP3A-inducing anti-epileptic drugs were not eligible. Twenty-five patients with recurrent MG were enrolled, including 15 (60%) with glioblastoma (GBM) and 10 (40%) with grade 3 MG. Five patients progressed previously on bevacizumab and two had received prior VEGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. The MTD was 50 mg of sunitinib combined with 75 mg/m2 of irinotecan. DLT were primarily hematologic and included grade 4 neutropenia in 3 patients and one patient with grade 4 thrombocytopenia. Non-hematologic DLT included grade 3 mucositis (n = 1) and grade 3 dehydration (n = 1). Progression-free survival (PFS)-6 was 24% and only one patient achieved a radiographic response. The combination of sunitinib and irinotecan was associated with moderate toxicity and limited anti-tumor activity. Further studies with this regimen using the dosing schedules evaluated in this study are not warranted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Anaplastic astrocytoma
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CR:
-
Complete response
- DLT:
-
Dose-limiting toxicity
- EIAEDs:
-
Enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- ITT:
-
Intent-to-treat
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky performance status
- MG:
-
Malignant glioma
- MTD:
-
Maximum tolerated dose
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PD:
-
Progressive disease
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PDGFR:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor receptor
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- PR:
-
Partial response
- SD:
-
Stable disease
- TTP:
-
Time to progression
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
References
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Ballman KV, Buckner JC, Brown PD, Giannini C, Flynn PJ, LaPlant BR, Jaeckle KA (2007) The relationship between six-month progression-free survival and 12-month overall survival end points for phase II trials in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Neurooncology 9:29–38
Lamborn KR, Yung WK, Chang SM, Wen PY, Cloughesy TF, Deangelis LM, Robins HI, Lieberman FS, Fine HA, Fink KL, Junck L, Abrey L, Gilbert MR, Mehta M, Kuhn JG, Aldape KD, Hibberts J, Peterson PM, Prados MD (2008) Progression-free survival: an important end point in evaluating therapy for recurrent high-grade gliomas. Neurooncology 10:162–170
Wu W, Lamborn KR, Buckner JC, Novotny PJ, Chang SM, O’Fallon JR, Jaeckle KA, Prados MD (2010) Joint NCCTG and NABTC prognostic factors analysis for high-grade recurrent glioma. Neurooncology 12:164–172. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nop019
Brem S, Cotran R, Folkman J (1972) Tumor angiogenesis: a quantitative method for histologic grading. J Natl Cancer Inst 48:347–356
Plate KH, Breier G, Millauer B, Ullrich A, Risau W (1993) Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor and its cognate receptors in a rat glioma model of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 53:5822–5827
Stefanik DF, Fellows WK, Rizkalla LR, Rizkalla WM, Stefanik PP, Deleo AB, Welch WC (2001) Monoclonal antibodies to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and the VEGF receptor, FLT-1, inhibit the growth of C6 glioma in a mouse xenograft. J Neurooncol 55:91–100
Takano S, Tsuboi K, Matsumura A, Nose T (2003) Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody and nimustine as combined therapy: effects on tumour growth and angiogenesis in human glioblastoma xenografts. Neurooncology 5:1–7
Kreisl TN, Kim L, Moore K, Duic P, Royce C, Stroud I, Garren N, Mackey M, Butman JA, Camphausen K, Park J, Albert PS, Fine HA (2009) Phase II trial of single-agent bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab plus irinotecan at tumor progression in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:740–745
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:4733–4740
Goodman VL, Rock EP, Dagher R, Ramchandani RP, Abraham S, Gobburu JV, Booth BP, Verbois SL, Morse DE, Liang CY, Chidambaram N, Jiang JX, Tang S, Mahjoob K, Justice R, Pazdur R (2007) Approval summary: sunitinib for the treatment of imatinib refractory or intolerant gastrointestinal stromal tumors and advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:1367–1373. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2328
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE II, Dowell JM, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S, Gururangan S, Wagner M, Bigner DD, Friedman AH, Friedman HS (2007) Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 13:1253–1259
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE II, Marcello J, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S, Gururangan S, Sampson J, Wagner M, Bailey L, Bigner DD, Friedman AH, Friedman HS (2007) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 25:4722–4729
Gilbert MR, Supko JG, Batchelor T, Lesser G, Fisher JD, Piantadosi S, Grossman S (2003) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan in adults with recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 9:2940–2949
Prados MD, Yung WK, Jaeckle KA, Robins HI, Mehta MP, Fine HA, Wen PY, Cloughesy TF, Chang SM, Nicholas MK, Schiff D, Greenberg HS, Junck L, Fink KL, Hess KR, Kuhn J (2004) Phase 1 trial of irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma: a North American Brain Tumor Consortium study. Neurooncology 6:44–54
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963–1972
Fleming TP, Saxena A, Clark WC, Robertson JT, Oldfield EH, Aaronson SA, Ali IU (1992) Amplification and/or overexpression of platelet-derived growth factor receptors and epidermal growth factor receptor in human glial tumors. Cancer Res 52:4550–4553
Hermanson M, Funa K, Hartman M, Claesson-Welsh L, Heldin CH, Westermark B, Nister M (1992) Platelet-derived growth factor and its receptors in human glioma tissue: expression of messenger RNA and protein suggests the presence of autocrine and paracrine loops. Cancer Res 52:3213–3219
Martinho O, Longatto-Filho A, Lambros MB, Martins A, Pinheiro C, Silva A, Pardal F, Amorim J, Mackay A, Milanezi F, Tamber N, Fenwick K, Ashworth A, Reis-Filho JS, Lopes JM, Reis RM (2009) Expression, mutation and copy number analysis of platelet-derived growth factor receptor A (PDGFRA) and its ligand PDGFA in gliomas. Br J Cancer 101:973–982
Dai C, Celestino JC, Okada Y, Louis DN, Fuller GN, Holland EC (2001) PDGF autocrine stimulation dedifferentiates cultured astrocytes and induces oligodendrogliomas and oligoastrocytomas from neural progenitors and astrocytes in vivo. Genes Dev 15:1913–1925. doi:10.1101/gad.903001
Abramsson A, Lindblom P, Betsholtz C (2003) Endothelial and nonendothelial sources of PDGF-B regulate pericyte recruitment and influence vascular pattern formation in tumors. J Clin Investig 112:1142–1151
Furuhashi M, Sjoblom T, Abramsson A, Ellingsen J, Micke P, Li H, Bergsten-Folestad E, Eriksson U, Heuchel R, Betsholtz C, Heldin CH, Ostman A (2004) Platelet-derived growth factor production by B16 melanoma cells leads to increased pericyte abundance in tumors and an associated increase in tumor growth rate. Cancer Res 64:2725–2733
Joensuu H, Puputti M, Sihto H, Tynninen O, Nupponen NN (2005) Amplification of genes encoding KIT, PDGFRalpha and VEGFR2 receptor tyrosine kinases is frequent in glioblastoma multiforme. J Pathol 207:224–231
Puputti M, Tynninen O, Sihto H, Blom T, Maenpaa H, Isola J, Paetau A, Joensuu H, Nupponen NN (2006) Amplification of KIT, PDGFRA, VEGFR2, and EGFR in gliomas. Mol Cancer Res 4:927–934
Socinski MA, Novello S, Brahmer JR, Rosell R, Sanchez JM, Belani CP, Govindan R, Atkins JN, Gillenwater HH, Pallares C, Tye L, Selaru P, Chao RC, Scagliotti GV (2008) Multicenter, phase II trial of sunitinib in previously treated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:650–656. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.13.9303
George S, Merriam P, Maki RG, Van den Abbeele AD, Yap JT, Akhurst T, Harmon DC, Bhuchar G, O’Mara MM, D’Adamo DR, Morgan J, Schwartz GK, Wagner AJ, Butrynski JE, Demetri GD, Keohan ML (2009) Multicenter phase II trial of sunitinib in the treatment of nongastrointestinal stromal tumor sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 27:3154–3160. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.9890
Faivre S, Raymond E, Boucher E, Douillard J, Lim HY, Kim JS, Zappa M, Lanzalone S, Lin X, Deprimo S, Harmon C, Ruiz-Garcia A, Lechuga MJ, Cheng AL (2009) Safety and efficacy of sunitinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: an open-label, multicentre, phase II study. Lancet Oncol 10:794–800. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70171-8
Machiels JP, Henry S, Zanetta S, Kaminsky MC, Michoux N, Rommel D, Schmitz S, Bompas E, Dillies AF, Faivre S, Moxhon A, Duprez T, Guigay J (2010) Phase II study of sunitinib in recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: GORTEC 2006-01. J Clin Oncol 28:21–28. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.23.8584
Gore ME, Hariharan S, Porta C, Bracarda S, Hawkins R, Bjarnason GA, Oudard S, Lee SH, Carteni G, Nieto A, Yuan J, Szczylik C (2011) Sunitinib in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients with brain metastases. Cancer 117:501–509. doi:10.1002/cncr.25452
Thibault F, Billemont B, Rixe O (2008) Regression of brain metastases of renal cell carcinoma with antiangiogenic therapy. J Neurooncol 86:243–244. doi:10.1007/s11060-007-9449-5
Koutras AK, Krikelis D, Alexandrou N, Starakis I, Kalofonos HP (2007) Brain metastasis in renal cell cancer responding to sunitinib. Anticancer Res 27:4255–4257
de Bouard S, Herlin P, Christensen JG, Lemoisson E, Gauduchon P, Raymond E, Guillamo JS (2007) Antiangiogenic and anti-invasive effects of sunitinib on experimental human glioblastoma. Neurooncology 9:412–423
Chahal M, Xu Y, Lesniak D, Graham K, Famulski K, Christensen JG, Aghi M, Jacques A, Murray D, Sabri S, Abdulkarim B (2010) MGMT modulates glioblastoma angiogenesis and response to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Neurooncology 12:822–833
Strawn LM, Kabbinavar F, Schwartz DP, Mann E, Shawver LK, Slamon DJ, Cherrington JM (2000) Effects of SU101 in combination with cytotoxic agents on the growth of subcutaneous tumor xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 6:2931–2940
Zhou Q, Guo P, Gallo JM (2008) Impact of angiogenesis inhibition by sunitinib on tumor distribution of temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res 14:1540–1549
Neyns B, Sadones J, Chaskis C, Dujardin M, Everaert H, Lv S, Duerinck J, Tynninen O, Nupponen N, Michotte A, De Greve J (2011) Phase II study of sunitinib malate in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. J NeuroOncol 103(3):491–501
Iwamoto FM, Lamborn KR, Robins HI, Mehta MP, Chang SM, Butowski NA, Deangelis LM, Abrey LE, Zhang WT, Prados MD, Fine HA (2010) Phase II trial of pazopanib (GW786034), an oral multi-targeted angiogenesis inhibitor, for adults with recurrent glioblastoma (North American Brain Tumor Consortium Study 06-02). Neurooncology 12:855–861. doi:10.1093/neuonc/noq025
Batchelor T, Mullholland P, Neyns B, Nobors LB, Campone M, Wick A, Mason W, Xu J, Liu Q, van den Bent M A phase III randomized study comparing the efficacy of cediranib as monotherapy, and in combination with lomustine, with lomustine along in recurrent glioblastoma patients. Ann Oncol 21(Suppl 8):viii4. Abstract number LBA7
Batchelor TT, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ancukiewicz M, Plotkin SR, Gerstner E, Eichler AF, Drappatz J, Hochberg FH, Benner T, Louis DN, Cohen KS, Chea H, Exarhopoulos A, Loeffler JS, Moses MA, Ivy P, Sorensen AG, Wen PY, Jain RK (2010) Phase II study of cediranib, an oral pan-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28:2817–2823. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.3988
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH Grants NS20023 and CA11898; NIH Grant MO1 RR 30, GCRC Program, NCRR; NIH SPORE Grant 5 P50 CA 108786-4 and a grant from Pfizer, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reardon, D.A., Vredenburgh, J.J., Coan, A. et al. Phase I study of sunitinib and irinotecan for patients with recurrent malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 105, 621–627 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0631-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0631-4