Abstract
Objective ATRX is a multifunctional protein that is tightly regulated by and implicated in transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling. Numerous studies have shown that genetic alterations in ATRX play a significant role in gliomas. This study aims to further determine the relationship between ATRX and glioma prognosis and identify possible mechanisms for exploring the biological significance of ATRX using large data sets.
Methods We used The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and 130 immunohistochemical results to confirm the difference in ATRX mutations in high- and low-grade gliomas. An online analysis of the TCGA glioma datasets using the cBioPortal platform was performed to study the relationship between ATRX mutations and IDH1, TP53, CDKN2A and CDKN2B mutations in the corresponding TCGA glioma dataset. In combination with clinical pathology data, the biological significance of the relationships were analyzed. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses and annotations of all adjacent genes in the network were performedin the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) and R language. A protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed, and the interactions of all adjacent nodes were analyzed by the String database and using Cytoscape software.
Results In the selected TCGA glioma datasets, a total of 2,228 patients were queried, 21% of whom had ATRX alterations, which co-occurred frequently with TP53 and IDH1 mutations. ATRX alterations are associated with multiple critical molecular events, which results in a significantly improved overall survival (OS) rate. In low-grade gliomas, ATRX mutations are significantly associated with multiple important molecular events, such as ZNF274 and FDXR at mRNA and protein levels. A functional cluster analysis revealed that these genes played a role in chromatin binding and P53, and a link was observed between ATRX and IDH1 and TP53 in the interaction network. ATRX and TP53 are important nodes in the network and have potential links with the blood oxygen imbalance.
Conclusions ATRX mutations have clinical implications for the molecular diagnosis of gliomas and can provide diagnostic and prognostic information for gliomas. ATRX is expected to serve as a new therapeutic target.
keywords
Introduction
Glioma is the most common primary malignancy of the central nervous system (CNS), with high heterogeneity and extensive mutations1. Despite combined surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and targeted therapy, the clinical efficacy and prognosis of gliomas are always poor2,3. Therefore, there is an urgent need to improve the clinical management of the disease4. In the molecular classification of gliomas, there is growing concern about the biological properties of this malignancy. To explore the molecular mechanism and novel biomarkers of gliomas to predict prognosis is a strategy to improve the diagnosis and treatment of glioma patients5. Genetic alterations play an important role in the development and progression of tumors6,7. Through a comprehensive analysis of genomic events, we can identify subgroups of certain tumor types and find correlations among clinical information to provide reliable prognostic markers and promising therapeutic targets8. In 2016, the WHO used molecular diagnosis at the center of a new classification of CNS tumors and introduced the ATRX mutation while exploring the diagnostic significance of mutant/wild-type IDH1 for glioma classification9–11.
ATRX belongs to the SWI/SNF family of chromatin-remodeling proteins, and the protein encoded by this gene contains an ATPase/helicase domain12. Mutations in this gene are associated with X-linked syndromes exhibiting cognitive disabilities as well as alpha-thalassemia (ATRX) syndrome. These mutations cause diverse changes in the DNA methylation pattern, which may provide a link between gene expression in developmental processes, DNA methylation and chromatin-remodeling13–15. ATRX is a major component of many critical cellular pathways, and new evidence shows that it not only functions as a molecular chaperone but is also critical in DNA replication and repair, advanced chromatin regulation, and gene transcriptional regulation16. This gene is involved in a wide range of biological processes, and the occurrence of ATRX mutations can cause changes in the molecular and clinical aspects of tumor characteristics. Mutations in regulatory factors occur frequently in gliomas, suggesting that epigenetic rearrangement is an essential event in glioma development. Studies have found that ATRX deletions/mutations are associated with a number of conventional molecular events, including IDH1 mutations and TP53 mutations17,18. Mukherjee et al.14 showed that the deletion of ATRX and the expression of mutant IDH1 are sufficient to produce tumorigenic cells with alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) characteristics. In addition, some studies have noted that ATRX mutation and CDKN2A deletion are closely related to the OS rate of patients with astrocytoma19–22.
Although numerous studies have shown the importance of ATRX in glioma, there is still a lack of comprehensive and systematic research on ATRX mutations. High-throughput data should be used to compare patients clinical data with ATRX mutation status16,23. In this study, we used The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and the online analysis tool cBioPortal to explore the biological significance of ATRX deletions/mutations in gliomas and their correlation with other eminent molecular events24,25.
Materials and methods
Access to bioinformatics data
This study utilized the cBioPortal platform to perform online analysis of glioma datasets from the TCGA. There were 2,228 samples with available mutations and copy number variation (CNV) data in the corresponding TCGA glioma datasets. Cases with ATRX, IDH1, TP53, CDKN2A and CDKN2B mutations were selected, and the mutation query was performed by OncoPrint function. The cancer types summary showed the types and distribution of mutations in different datasets. Comparative analysis of brain low-grade glioma (LGG) and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) plots illustrated the correlation of CNV/mutation versus mRNA expression. The survival was explored by Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival. The enrichment function showed alterations including copy number alterations, mutations, mRNA expression changes, and protein expression alterations that contained both altered and unaltered queried samples. The network illustrated the interactions between queried genes and all neighboring genes. The Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery [(DAVID), v 6.8 https://david.ncifcrf.gov/summary.jsp] was used for clustering of all neighbor genes being queried in the network. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed by the String database ( https://string-db.org/), and the interactive relationship of all the neighboring nodes in the network was calculated and demonstrated by Cytoscape software.
Specimens and reagents
A total of 130 samples of glioma patients who underwent surgery from 2015 to 2018 in the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University were gathered. All cases received the support of pathological diagnosis, including 3 cases of WHO I, 62 cases of WHO II, 17 cases of WHO III, and 48 cases of WHO IV. According to the 2016 WHO classification criteria for CNS tumors, immunohistochemistry IDH1 was performed, which was split into IDH1 mutant-type 47 cases and IDH l wild-type 83 cases. Anti-human IDH1 (R132H) antibody (ZM-0447), rabbit anti-human P53 antibody (ZM-0501) and rabbit anti-human ATRX antibody (ZA-0016), Universal two-step test kit (PV-9000) and DAB stain were obtained from OriGene Technologies, Inc. (Beijing, China). The pathological tissue specimens involved in the study were subject to approval by the Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University and met the ethical requirements.
Immunohistochemical studies
Tumor tissues were fixed in 10% formaldehyde at room temperature for 24 h, embedded in paraffin and cut into 3.5 µm thick sections. For immunohistochemistry, primary antibodies were utilized according to the manufacturer's protocol. Each section was blocked with 3% hydrogen peroxide at 37°C for 10 min. Sections were incubated with the primary antibody overnight at 4°C. Subsequently, sections of Goat Anti-Mouse / Rabbit IgG antibody were incubated for 30 min at room temperature with a 1:100 dilution. The staining was observed using a Nikon microscope (Nikon Corporation, Tokyo, Japan; magnification, ՠ40). P53, ATRX and IDH1 were scored using a four-level scale, which quantifies the percentage of stained nucleus / cytoplasm and classifies them into one of four categories: (), < 10% of nucleus / cytoplasm staining, which indicates no immunoreactivity; (l +), 10%30% of nucleus / cytoplasm stained; (2 +), 30.1%50% of nucleus / cytoplasm stained; (3 +), > 50% of nucleus / cytoplasm stained. ATRX (2 +) and (3 +) were considered positive, and P53 (), IDH1 () was considered negative. Positive and negative controls were established for immunohistochemistry of all specimens 26,27.
Statistical analysis
All online statistical analyses were performed automatically by the cBioPortal platform, and P values < 0.05 and q values < 0.05 were accepted as statistically significant. Immunohistochemical results were analyzed using IBM SPSS statistics software V 22.0. Pearson χ2 test or Fishers exact test was used for comparison of categorical variables, and P < 0.05 was statistically significant.
Results
Comutation of ATRX with IDH1 and TP53 mainly occurs in LGG
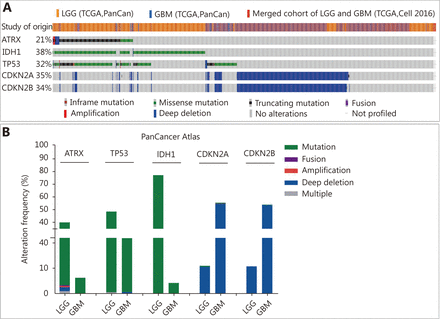
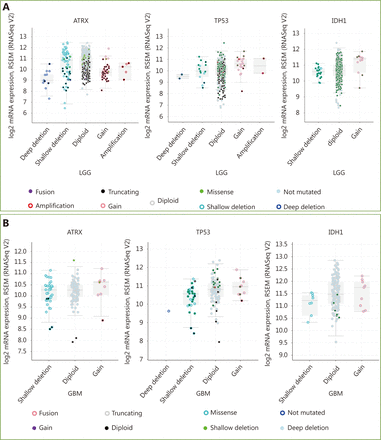
Three datasets were selected from the TCGA CNS tumor datasets for a total of 2,228 samples. There were 1,721 (77%) samples with ATRX, IDH1, TP53, CDKN2A, and CDKN2B mutations and CNV data in the corresponding TCGA glioma datasets. ATRX mutations were found in approximately 21% of the samples, with truncating mutations and deletions being the major type of alteration. The IDH1 mutation accounted for 38%, the TP53 mutation accounted for 32%, and the CDKN2A and CDKN2B depth deletions were approximately 35% and 34%, respectively (Figure 1A). We found that the co-occurrence of IDH1, TP53 and ATRX mutations mainly occurred in LGG (TCGA, Pan-Cancer). Subsequently, we examined the changes in the three genes ATRX, IDH1, and TP53. The analysis of the LGG (TCGA, Pan-Cancer) and GBM (TCGA, Pan-Cancer) datasets showed that the mutation frequency of the three genes in the LGG group was significantly higher than that in the GBM group (Figure 1B). The plot function illustrated the corresponding mRNA levels associated with the CNVs/mutations of ATRX, TP53 and IDH1. The results show that deep deletions and truncation mutations of ATRX in LGGs are associated with low mRNA expression levels. Deletion and amplification of TP53 are associated with expression levels, but the incidence of mutations is low, and amplification of IDH1 is associated with high mRNA expression levels (Figure 2A). In GBM, CNV/mutations in the three genes are involved in mRNA expression, but the frequency of mutations is significantly lower than that in the LGG group. There were no ATRX deep deletions or TP53 amplifications in GBM (Figure 2B).
Changes in ATRX, TP53 and IDH1 genes in glioma. (A) Genetic status of ATRX, TP53, IDH1, CDKN2A and CDKN2B in glioma patients. (B) Frequency of ATRX, TP53, IDH1, CDKN2A and CDKN2B alteration in LGGs and glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
mRNA level was consistent with gene change. (A) Functional plotting of the corresponding mRNA level in relation to genetic status of ATRX, TP53 and IDH1 of LGGs; (B) Functional plotting of the corresponding mRNA level in relation to genetic status of ATRX, TP53 and IDH1 of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
ATRX mutation is associated with glioma prognosis
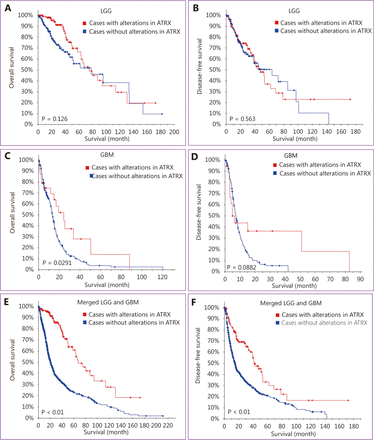
We searched the TCGA dataset containing clinical information on glioma patients and performed survival analysis of those with LGG (TCGA, Provisional) and GBM (TCGA, Provisional). The results showed no significant difference in OS or disease-free survival (DFS) among the LGG (TCGA, Provisional) cases (Figure 3A, B). In GBM (TCGA, provisional), the OS of the ATRX mutant group was higher than that of the unstated group (Figure 3C), but there was no significant difference in DFS (Figure 3D). Analysis of the integrated dataset of LGG (TCGA, Provisional) and GBM (TCGA, Provisional) cases showed more significant differences; the OS and DFS of cases with ATRX mutations were significantly higher than those of the without ATRX mutations group (Figure 3E and 3F). We thought that the survival analysis of LGGs was not significantly different due to longer shelf-life and ubiquitous IDH1 mutations. Survival analysis in the GBM group showed that patients with ATRX mutations had a relatively good prognosis, which is expected to be very valuable. Integration analysis of survival also suggests that ATRX mutations can be utilized to judge prognosis and even provide indications for clinical pathological grade.
Patients with ATRX alteration gliomas have a better prognosis.
ATRX loss in different grades of glioma
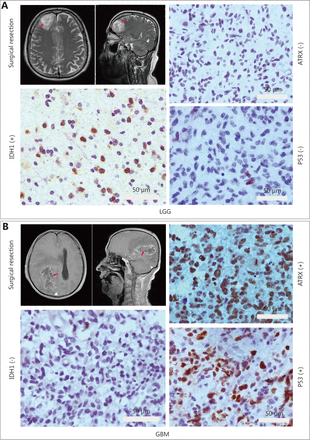
Immunohistochemical studies have shown that ATRX loss is more common in mutant IDH1 gliomas but is rare in wild-type IDH1 gliomas. Anti-IDH1-R132H positive immunostaining was regarded as IDH1 mutation status in human gliomas. Negative controls were performed using PBS without the primary antibody. The incidence of ATRX deletions was 42.6% (20/47) and 22.9% (19/83), respectively (P < 0.05), which was statistically significant. The incidence of P53 overexpression in IDH1 mutant and wild-type gliomas was 42.6% (20/47) and 36.1% (30/83), respectively, with no significant difference ( Table 1 and Figure 4). ATRX loss is more common in LGGs (WHO I & II) but relatively rare in high-grade gliomas (WHO III&IV). The incidence of ATRX loss was 40.0% (26/65) and 20.0% (13/65) ( P < 0.05), and the incidence of P53 overexpression in high-grade gliomas and LGGs was 50.8% (33/65) and 26.2% (17/65), respectively ( P < 0.05). There are significant differences between the groups ( Table 2 and Figure 4).
Expression of ATRX and P53 in gliomas with mutant and wild-type IDH1
IHC staining for ATRX, TP53 and IDH1. (A) Low-grade glioma image localization and immunohistochemistry. (B) Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) image localization and immunohistochemistry. Gray bar: 50 µm.
Expression of ATRX and P53 in different grades of glioma
ATRX mutations are associated with multiple molecular events in LGGs
Built on the above analysis, we found that ATRX deletion/mutation mainly occurs in LGG (TCGA, Pan-Cancer) and is associated with patient prognosis. In addition, ATRX is often co-mutated with IDH1 and TP53, so we further explored the interaction of ATRX mutations with IDH1 and TP53 in LGGs.
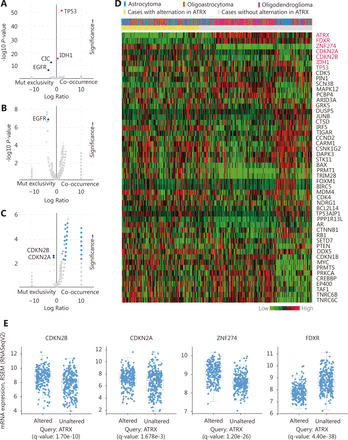
The enrichment function indicated that there was a significant positive correlation among IDH1, TP53 and ATRX in gene mutations. Interestingly, we also found significant mutual exclusivity between CIC and EGFR mutations and ATRX mutations (Figure 5A). In the CNV, we suggest that EGFR mutations are primarily negatively correlated with ATRX amplification (Figure 5B). There is a mutual exclusivity among CDKN2A, CDKN2B and ATRX deep deletion changes (Figure 5C). However, the correlations between ATRX and IDH1 and TP53 are not included in the change of copy number.
Relationship between ATRX alter and other genetic alternation. (A) ATRX alterations are positively correlated with alterations in TP53 and IDH1 but negatively correlated with changes in CIC and EGFR. (B) EGFR is negatively correlated with ATRX amplification changes. (C) CDKN2A, CDKN2B is negatively correlated with ATRX deletion alterations. (D) Relationship between ATRX alteration and pathological tissue types of patients and changes in mRNA expression profiles of related genes after ATRX changes. (E) mRNA-related genes (CDKN2A,CDKN2B.ZNF274 and FDXR) change significantly after the alteration in ATRX; statistically significant, q-value < 0.05.
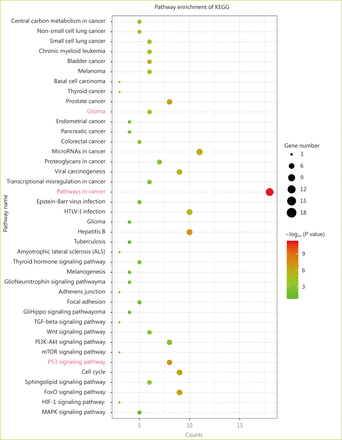
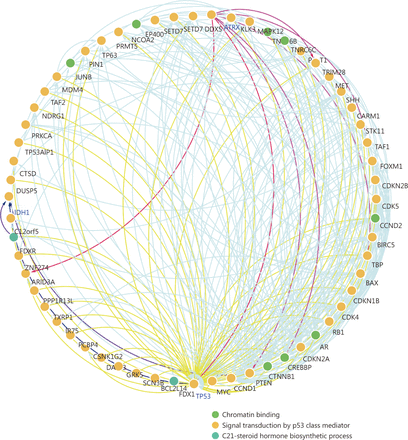
Through the network tab, we searched for all neighboring genes associated with ATRX mutation-related genes (IDH1, TP53, CDKN2A, CDKN2B). There are 55 neighboring genes in the list. These genes were input into the OncoPrint function for mRNA cluster analysis, and the results showed that the deletion mutation of ATRX was associated with a decrease in mRNA expression. However, the mRNA expression levels of IDH1 and TP53 were not significantly correlated with their mutations, which may be related to the different incidence of mutation types. In the mRNA enrichment analysis, we also observed that astrocytoma types occurred more frequently in the ATRX-altered group than the unaltered group. ATRX changes were significantly positively correlated with mRNA expression (Figure 5D). In addition, ATRX was significantly negatively correlated with ZNF274, CDKN2A, and CDKN2B mRNA expression. A significant positive correlation was observed with FDXR (Figure 5E). All of the above results suggest that these genes may interact with ATRX mutations. When we entered into the list of neighboring genes into DAVID, we noticed that ATP binding was the most abundant biological process in ATRX mutation-related genes and plays a role in DNA damage repair and P53 binding. These related genes are involved in the development of tumors, such as glioma, bladder cancer, breast cancer, etc. and are closely linked to the P53 pathway, mTOR pathway, TGFݠpathway and cell cycle (Figure 6). Furthermore, we analyzed the protein interactions between ATRX mutation-related genes through the String database and used Cytoscape software annotation to show the relationship between them in the interaction network. ATRX and TP53 are important nodes in the network (Figure 7).
Enrichment analysis of the KEGG pathway between ATRX and its neighboring genes.
Protein-protein interaction network between ATRX and its neighboring genes.
Discussion
The ISN-Haarlem consensus proposes to officially introduce three molecular markers, ATRX, IDH1 and 1p19q, to declare gliomas into the era of molecular pathology diagnosis28. In 2016, the WHO supplemented the classification of CNS tumors and proposed new classifications based on histological and molecular characteristics, such as glioblastoma-IDH wild-type and glioblastoma-IDH mutant29,30. The new classification system adds molecular typing to the classification based on the histological classification. Integrating tissue phenotypes and genotype markers for CNS tumor classification improves the objectivity and personalization of diagnosis. Therefore, it is supposed to promote the accuracy of prognosis assessment and improve the clinical management of patients31,32. Hence, ATRX has also been widely studied recently. Liu et al.33 noted that the ATRX mutation is linked to age and is more common in adult diffuse glioma. Olar et al.34 reported that patients with ATRX mutations have higher survival rates in wild-type IDH1 adult gliomas. Although many studies have indicated that ATRX mutations can provide useful information for glioma prognosis, there remains a lack of systematic and clear understanding of ATRX research, and its molecular mechanism needs further exploration35.
In this study, we used the TCGA (Pan-Cancer) database to analyze the correlation between ATRX mutations and IDH1 and TP53 mutations by integrating a large amount of data. Combined with the immunohistochemical results of pathological samples and TCGA survival analysis, it was confirmed that ATRX mutation can be invoked as a reference for pathological grading and prognosis, and the role of ATRX mutation in the development of glioma is discussed36. We found that patients with ATRX mutations in the GBM group also had a better prognosis, suggesting that ATRX may be a novel therapeutic target, which is valuable37,38. In addition, we observed that P53 overexpression is more common in high-grade gliomas than in LGGs based on immunohistochemistry results, which are consistent with the report of Cho et al.39. In past studies, ATRX mutations/deletions were associated with the development of multiple cancers and involved in multiple biological processes40. We found that ATRX cooccurs with IDH1 and TP53 mutations in LGGs. Additionally, there is a significant negative correlation with EGFR and (Capicua) CIC mutations. Studies have shown that EGFR mutations are mainly found on amplification, mostly in GBM41. The Drosophila CIC gene is homologous to the 1p/19q codeletion, and CIC mutations occur more frequently in oligodendroglioma42. This study also suggests that ATRX and EGFR and CIC changes may occur in different types of glioma and can be utilized as indicators of molecular typing. The specific relationship between them has additional research value and clinical significance43,44.
In addition, ATRX is a chromatin-remodeling protein whose main function is the deposition of histone variant H3.345. The 3' exon of the zinc finger (ZNF) gene is a target of ATRX, and the H3K9me3 level in the ZNF gene is particularly sensitive to the inactivation of ATRX, which has the function of recruiting SETDB1, TRIM28 and zinc finger protein 274 (ZNF274)46. This study found that ZNF274 has a significant negative correlation with ATRX at the mRNA level, which further supports the interaction between ATRX and ZNF274. Notably, we found that the expression of FDXR mRNA is consistent with that of ATRX. Studies have shown that ATRX regulates the expression of two genes, HBA 1 and HBA 2, which are necessary for the production of hemoglobin47–49. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that delivers oxygen throughout the body's cells. FDXR is the only human ferredoxin reductase involved in ISC and heme biosynthesis, so ATRX and FDXR may be related to blood oxygen imbalance and affect the development of tumors. Studies have shown that p53 protein plays a role in iron homeostasis and is required for FDXR-mediated iron metabolism50. FDXR and P53 are mutually regulated, and the FDXR-P53 loop can inhibit tumors by iron homeostasis51. In the protein-protein interaction network, we also see the relationship between FDXR and IDH1. We speculate that ATRX and TP53 and IDH1 may interact with FDXR. The effect of the ATRX mutation on glioma may also be related to blood oxygen transport52. This information may provide an explanation for the phenomenon of ATRX, TP53, and IDH1 mutations, and furnish additional research ideas for blood oxygen imbalance with tumor progression53. However, all of these speculations are worthy of further study, specifically requiring experimental validation and more data support.
Conclusions
In summary, this study identified the genetic alterations in ATRX, IDH1 and TP53 as symbiotic characteristics through TCGA glioma datasets, which initially reflected the relationship of these tumor genes in mutation. The value of the ATRX mutation in prognostic evaluation was upheld. Additionally, we investigated the relationships between ATRX and TP53 and IDH1 mRNA expression and protein interaction levels in LGGs and further explored the correlation between ATRX mutations and other bimolecular events. These findings and speculations still require more experimental and data support, but at least our data systematically demonstrate the distribution and clinical significance of ATRX mutations in gliomas. ATRX has many intrinsic links with various significant molecules, such as IDH1 and TP53. In future studies, precise experimental analysis of these related genes should be carried out to provide a reference for the study of ATRX as a novel therapeutic target.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the Special Construction Innovation Funded Project for Community in Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei of China (Grant No. 18247792D) and the Hebei Basic Research Cooperation Project (Grant No. H2018201306). We sincerely appreciate the public experimental platform (Laboratory of Neuro-Oncology, Tianjin Neurological Institute, Tianjin, China; Medical Comprehensive Experimental Center of Hebei University, Baoding, China; Key Laboratory of Pathogenesis Mechanism and Control of Inflammatory-autoimmune Diseases in Hebei Province, Baoding, China) for providing experimental facilities.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Footnotes
↵These authors contributed equally to this work.
- Received April 8, 2019.
- Accepted July 19, 2019.
- Copyright: © 2019, Cancer Biology & Medicine
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) 4.0, which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.